Introduction to Programming (Using the C Language)
Welcome to the wonderful world of computer programming! This article serves as an introduction to programming (using the C language) and will introduce you to:
- The most basic definitions required to understand programming.
- Compilation and the creation of computer programs from text files.
- The errors that you might face if you are programming a computer.
A computer is a device designed to carry out calculations and to store and manipulate data. Programming is the discipline of writing sequences of instructions for those computers to execute. These sequences of instructions are called computer programs.
Programs are written in programming languages. A programming language is a way for humans to write code that can be interpreted by a computer.
A programming language specifies:
- The words and symbols that are used to write programs in that language.
- The rules for forming valid program statements.
A good analogy for this is writing a letter to a friend or relative. A written language, like English, specifies words and symbols (i.e. punctuation) that can be used, as well as rules to form statements that can be interpreted and understood by other readers.

A programming language has a certain set of words, symbols, and rules that combine to create a program that can be interpreted by a computer.

These programs are stored as files on the computer (e.g. on the hard disk). Broadly speaking, there are two different types of files related to programs:
- Source files are text files written in a programming language. They cannot be executed.
- Executable files (or binaries) are produced from the source file by a compiler and can be executed by the computer.
To be translated from a language that is readable and writable by humans into an executable that can be ran by a machine, programs must be compiled.
Computers only understand instructions in the language of their central processing unit (or CPU). This is called assembly language. Assembly language is not very easy or intuitive for humans to read or write so we have created other higher-level programming languages that are.
If a programming language is written in code that is close to that of assembly language, we say it is a low-level language.
If a programming language is written in a way that is easy and intuitive for humans to understand, we say it is a high-level language.
There are hundreds of programming languages crossing the spectrum from extremely low level to extremely high-level languages.
C is a relatively low-level program language (though not as low as assembly language!). When writing in the programming language we are writing in words and symbols that match very closely to the fundamental operations that are carried out by a central processing unit. This makes it a great choice for your first programming language!
So, first the programmer writes some basic source code that will (hopefully!) compile. The programmer then runs the compiler to turn the source code into an executable file. This executable file can then be run by any user, executing the program.
Computers are very literal. A computer program will only run if it follows the rules of the language (also known as its syntax). This syntax defines how symbols, identifiers, and reserved words may be used together to form a valid program.
If the programmer makes a mistake in the arrangement of these symbols, identifiers, and reserved words, the result will be a syntax error and often the program will refuse to compile until the error is corrected.
A computer program will always do what it is told to do. Sometimes, if the programmer makes a mistake, this can be different from what the programmer intended. The semantics of a program statement are what that statement will do when it is executed.
If the programmer’s syntax is correct but they have made a mistake in their logic that makes the program behave in a way that they did not intend, then this is a semantic error.
Broadly speaking, there are three types of errors a programmer may make when programming:
- Syntax errors (compiler errors) result when the programmer uses bad syntax. This will result in a compiler error, and the compiler will fail to make the executable file from the source code.
- Run-time errors are errors that occur during program execution, such as when the program attempts to divide by zero or gets unexpected input from a user. These result in the program crashing while running.
- Semantic or logical errors are when the programmer has made a mistake in their logic. The program will run but will not produce the expected results.
If a program contains an error, it is up to the programmer to fix or “debug” the error and then recompile the program.
If the program contains no errors, then the programmer has created a software application that executes their programming statements and does exactly what the programmer intends.
Good programming is a repetitive process of writing a small amount of code, checking that it compiles and behaves as expected, fixing any errors, and then repeating the process.
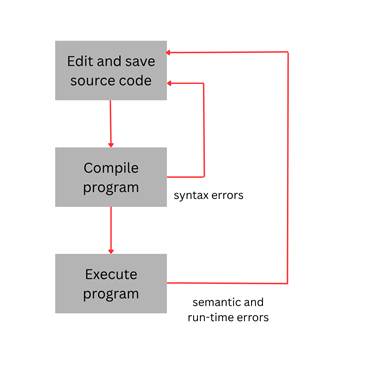
This results in the gradual, iterative building of the complete program the programmer is trying to implement.
I hope you enjoyed this introduction to programming (using the C language). If you want to check out similar content, here is a link to my blog.
If you wish to receive these articles as an email newsletter, subscribe to my mailing list here.
I wish you all the best in your journey of learning and self-discovery.
