Computers, Hardware, Software, and Operating Systems
This article teaches the basics of computers, hardware, software and operating systems.

Computers are a form of digital technology designed to carry out computations and to store and manipulate data.
Computers store values in memory as binary numbers: strings of zeroes and ones. These binary zeroes and ones can be used to represent anything from real numbers, to text, to web pages, music, and video.
Software stored as binary can be executed on a computer to perform mathematical and logical operations by communicating with a central processing unit (or CPU).
Here are some things even simple computers can do:
- Perform arithmetic calculations like adding, subtracting, multiplying, or dividing.
- Store, retrieve, and manipulate data.
- Make decisions and perform actions based on data and logic.
- Execute programs, which are sequences of the above actions.
Types of Computers
Computers come in many different shapes and sizes.
A computer might be a bulky desktop designed to sit on a table. These often have peripheral (i.e. external) devices such as keyboards and monitors.
Laptops are battery-powered computers designed to be more portable than laptops, ideal for use on the go.

Desktops and laptops are either PCs (personal computers) or Macs. Macs are desktops and laptops manufactured by Apple. A modern desktop or laptop that is not a Mac is generally called a PC, regardless of manufacturer.

Mobile devices are even more portable than laptops. They include smartphones and tablets.
Game consoles are mass-produced computers specifically designed to play video games on a television. Popular brands include Xbox, PlayStation, and Nintendo.
Wearables include smartwatches, fitness trackers, and smart glasses. They are small computers designed to worn as fashion accessories on a day-to-day basis.
Smart devices, appliances, and Internet of Things (IoT) devices are many and varied. There are countless devices containing computers and able to access the Internet, including smart TVs, fridges, and other appliances, as well as Internet-connected devices such as security cameras.
Servers are computers that serves up information to other computers on a network, such as a home network or the Internet. Websites are served to your web browser by a website from across the world using the Internet. Many businesses use local file servers to store their files and share them amongst employees.
Computer Hardware
Hardware is any part of a computer that has a physical structure, such as the keyboard, mouse, internal components of the computer, and even the computer’s casing.
At its most basic a computer is just hardware: a central processing unit, memory, and connections (or buses) to allow those things to communicate with each other. In a personal computer or laptop, these components are all connected by a main circuit board called a motherboard.
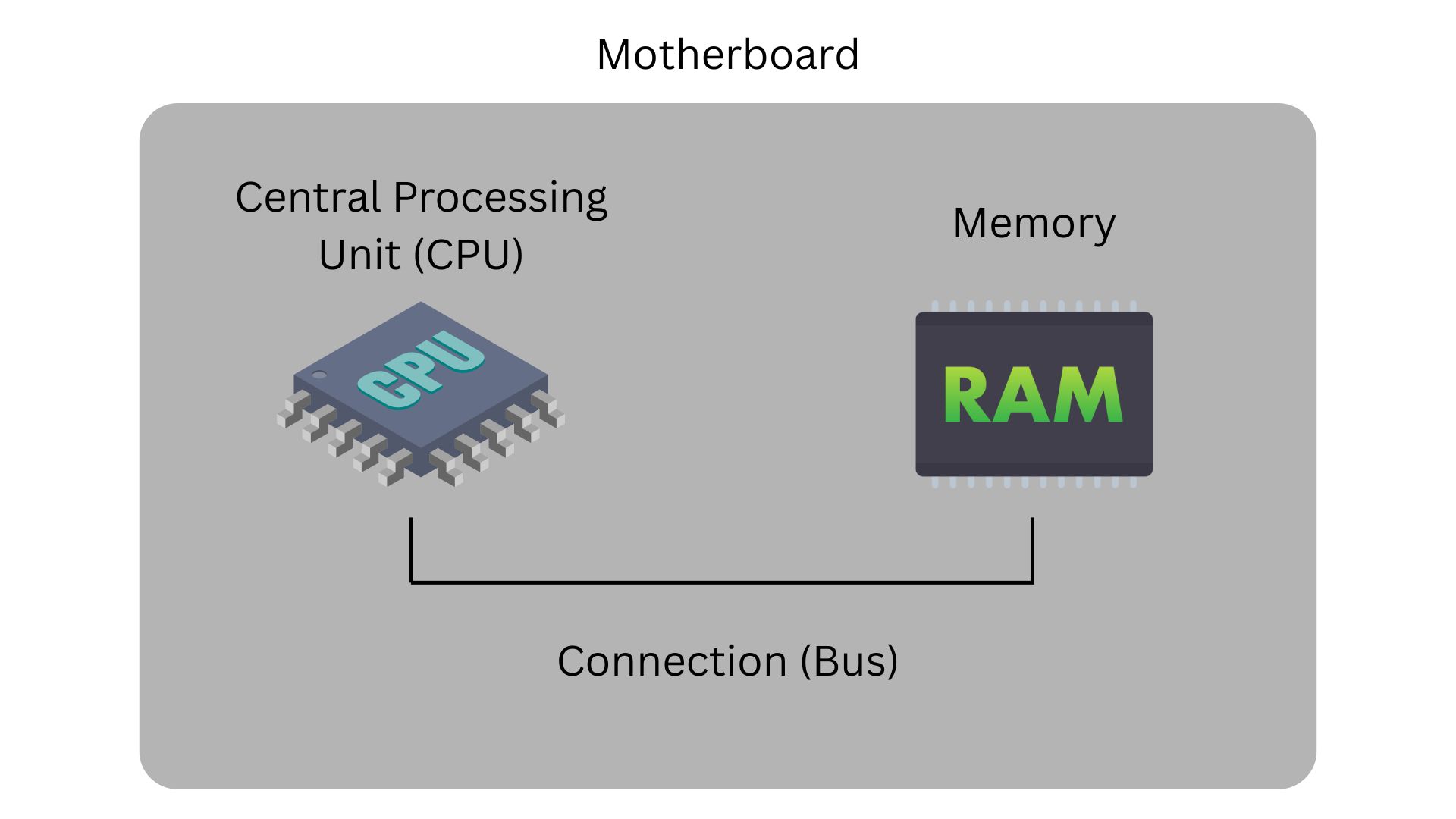
The central processing unit (or CPU) is the part of the computer that performs calculations and makes decisions. Whenever you press a key or click the mouse you send instructions to the CPU to execute. Processor speed is measured in megahertz (MHz) or millions of instructions per second. Gigahertz (GHz) is the number of billions of instructions per second. The ability of a computer to perform instructions at this speed may be restricted by other hardware, such as the memory or the connections between the CPU and the memory.
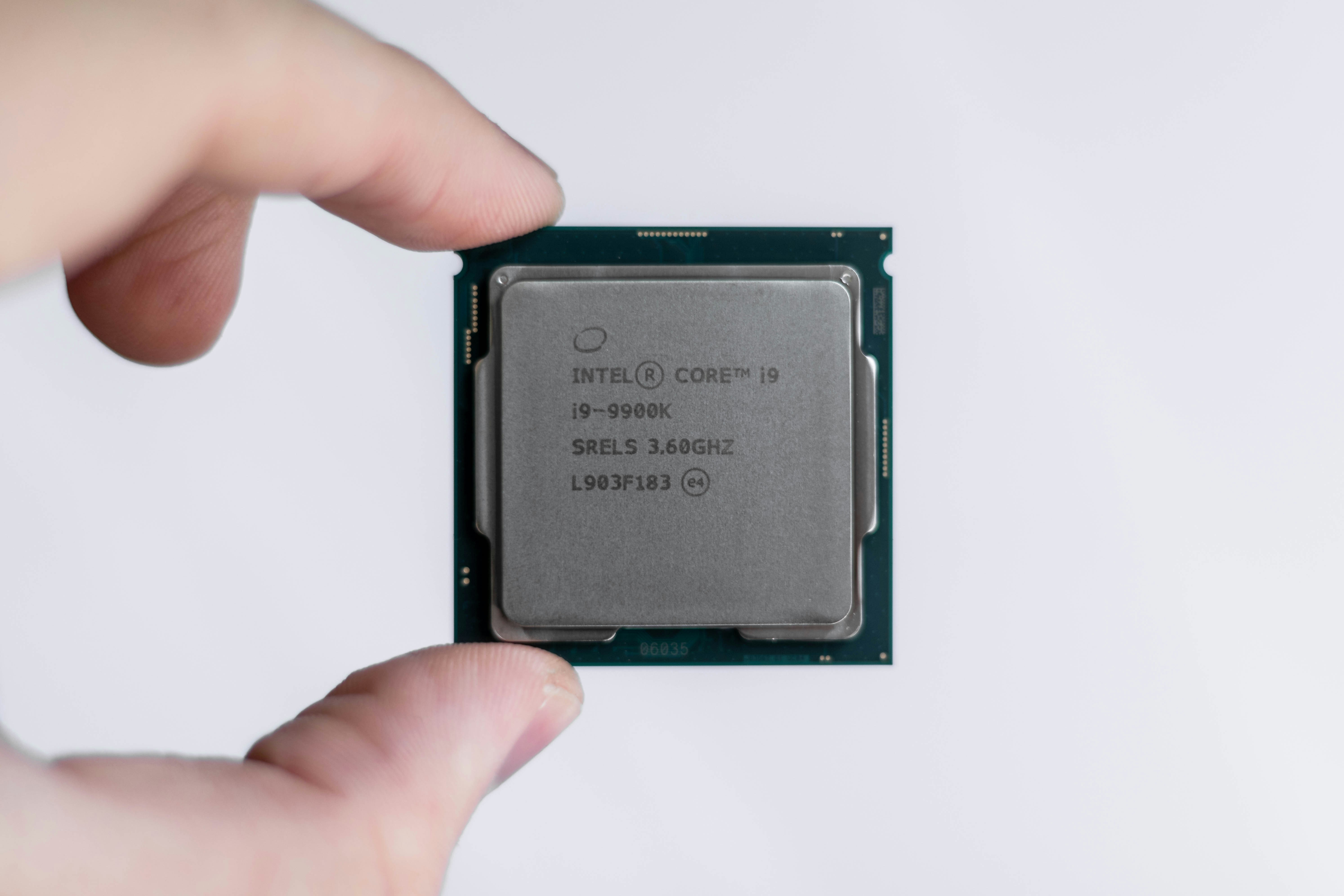

CPUs can get very hot and often covered with metal heat sinks to safely absorb and dissipate that heat.
Memory is how much data the computer can store. This includes programs, files, and data like values the computer is currently working with. Memory is measured in bits (a one or a zero) and bytes (sequences of eight bits).One thousand bytes make a kilobyte (kB), one million bytes make a megabyte (MB), one billion bytes make a gigabyte, and one trillion bytes make a terabyte (TB).
Modern computers are a bit more complicated than just a connected CPU and memory. For example, modern computers usually have both primary and secondary memory.
Primary memory is very fast but it is volatile, meaning that it is wiped clean and forgotten when the computer is turned off or rebooted. Primary memory is usually random access memory (which is commonly shortened to RAM).
Secondary memory persists even when the computer reboots. It is long-term storage. Examples of this would be storage drives like a hard drive, a solid state drive, or a USB drive.
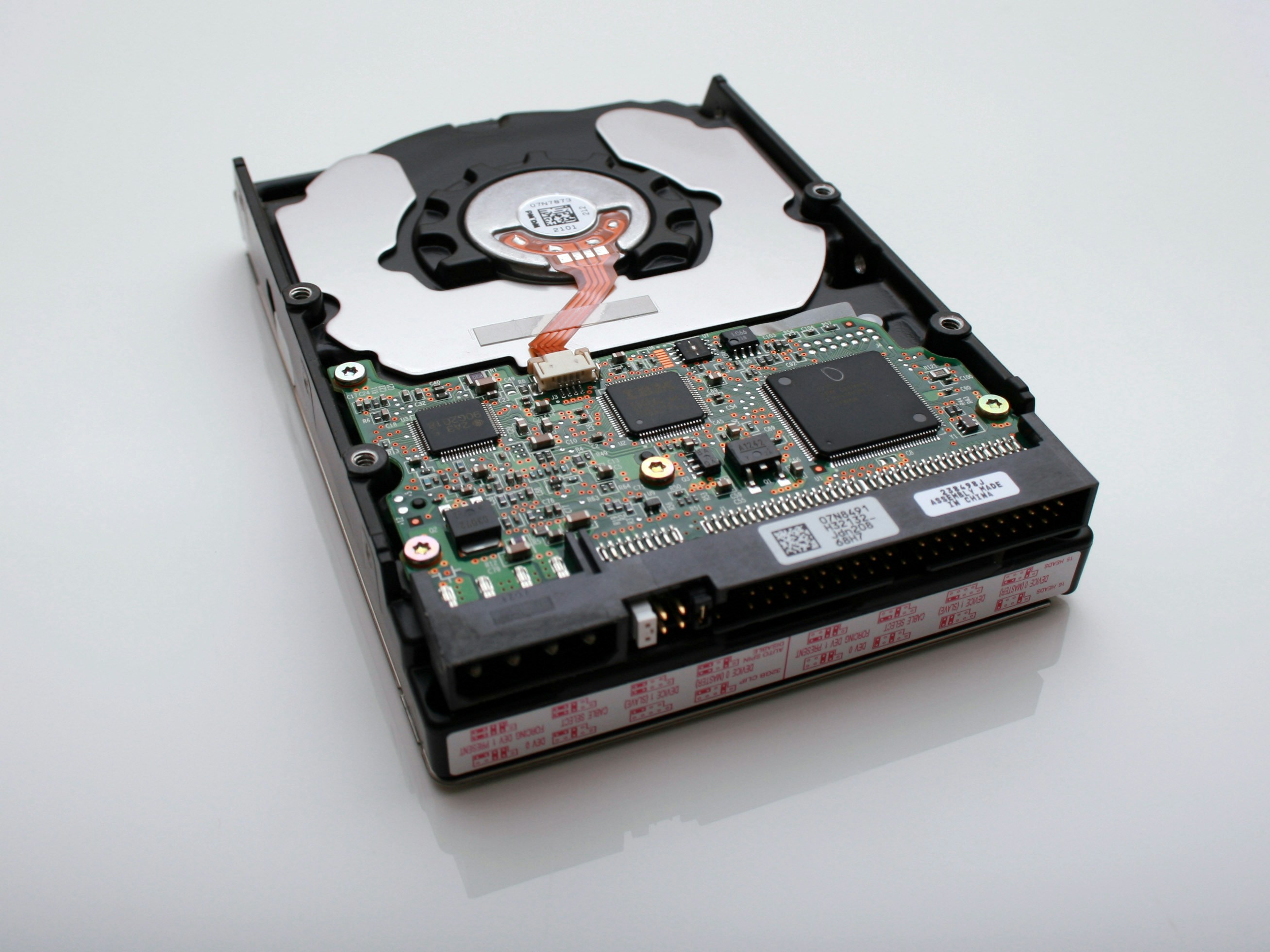

Files and software are stored in secondary memory, but when data is needed by a program it is retrieved and sent to the primary memory so it can be accessed more quickly by the CPU for use in calculations. Then, if necessary, the information is written back to secondary memory to update it for longer-term storage.
Modern computers may also have additional hardware components like power supplies, cables, fans, graphics cards, monitors, USB connectors, headphone jacks, optical drives, card readers, and more. But basic computers like calculators might still just consist of a CPU, primary memory, a power source (like a battery), and a case with a screen and buttons.
Hardware can be external (i.e. a peripheral device like a mouse or printer), internal (such as the CPU and memory), or built into your device’s case (like the keyboard and monitor of a laptop).
Computer Software
Software is a set of instructions that tells the hardware what to do. Software is stored in memory, where it sends calculations to the CPU to be performed.
Software can also be called programs, applications, or apps. When a software program is executed it becomes a process that does whatever it was programmed to do.
Software is essentially just a sequence of instructions and decision points for the computer that allow the software to do things with the CPU, memory, and other hardware. This might be running the web browser on your laptop, the banking app on your phone, or a video game on your PlayStation.

Software executes three main tasks on the CPU:
- Performing arithmetic calculations.
- Storing, retrieving, and manipulating data.
- Making decisions and performing actions based on data and logic.
The Operating System
There’s one more piece to this puzzle: the operating system.
The operating system is the interface between the hardware and the software. It is itself software, stored in memory, but it can control the hardware, and it can give access to that hardware to other programs. So, if your operating system allows it, you can run your favorite word processor, streaming service app, or game.
Examples of operating systems are Windows 11, Mac OS X, any of the various distributions of Linux. Generally, PCs are used to run Windows and Macs are used to run Mac OS X, and either PCs or Macs can be used to run Linux-based operating systems.

Phones have their own operating systems: iPhone runs on iOS, and many other phones use the Android operating system.
So:
- You have your hardware device, a computer, with its CPU and memory.
- You have your operating system running on top of that.
- You have the operating system giving your software access to your hardware.
- Your software runs on your device!
I hope you enjoyed this article! If you want to check out my other blog articles then click here.
If you want to receive these blog articles as a weekly newsletter, subscribe here.
